A Retail Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) is issued by the Central Bank to the general public for the sale and purchase of goods and services. It is a legal tender issued by the central bank in the form of digital currency intended only for retail users (for example to buy coffee or vegetables). This means that if an individual holds $100 CBDC, it is equivalent to $100 of cash notes. Conversion of cash to retail CBDC and vice versa is possible, which shall make the adoption of retail CBDC easier.
There are various models for the issuing, distribution, and management of retail CBDC and a country may choose to adopt a model that suits its ecosystem.
Retail CBDC can be designed to work either as Token based or Account based CBDC.
Account Based CBDC
Account-based CBDC works on the principles of the traditional mode of settlement. A payment request initiated by an individual undergoes validation, followed by a debit of the account, and finally, on the verification of the beneficiary, the credit of the amount happens.
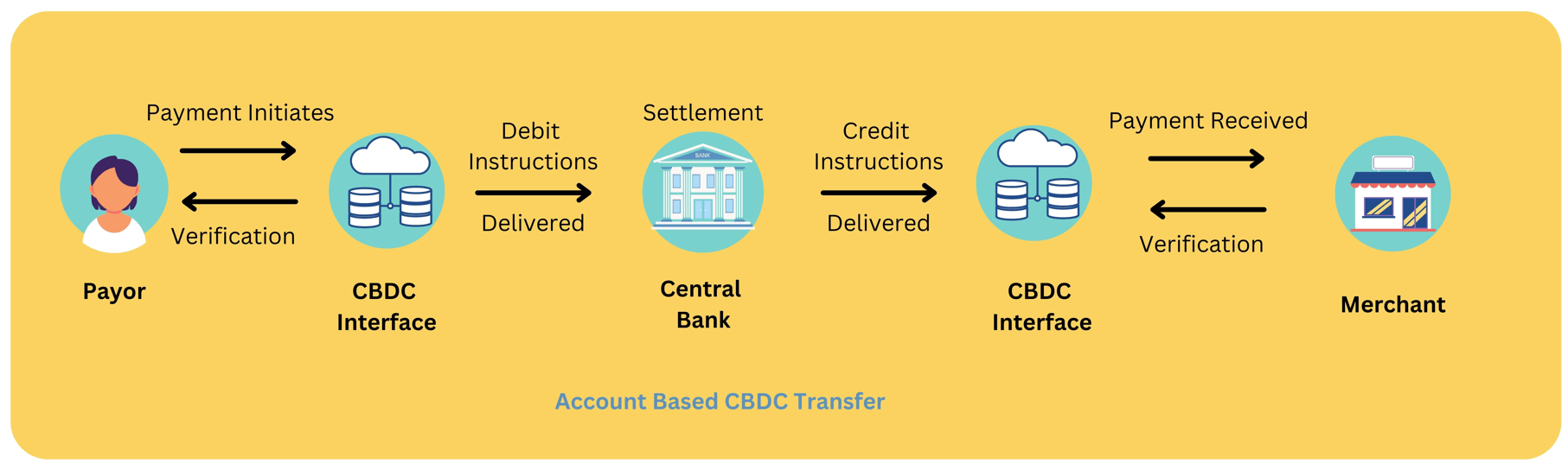
This method of transfer has a dependence on the banking relationship as the banks facilitate the debit and credit of the amount after the verification of the payor and the recipient, just like it happens in the transfer of money from one deposit account to another.
This means that for an account-based CBDC, an individual shall need to have an account in a bank.
Token Based CBDC
Token Based CBDC, as the name suggests, are digital tokens. An individual doesn’t really need a bank account to store Token based CBDCs as these are designed to be stored in digital wallets which can be operated using a private key.
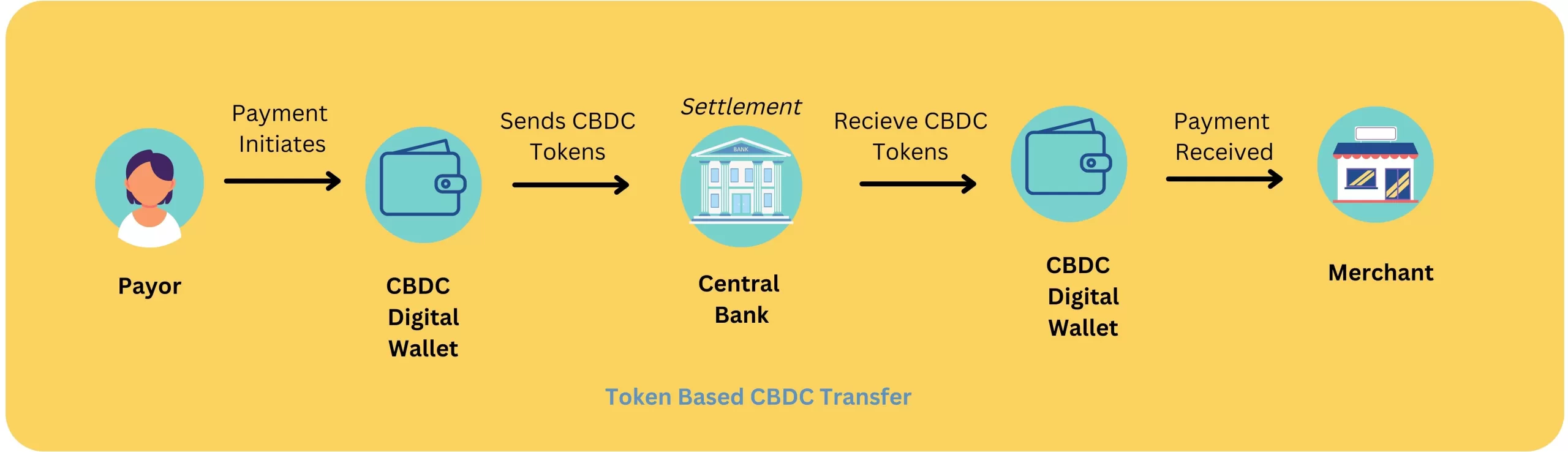
On making a transfer between one digital wallet and the other, real-time settlement of token CBDCs happens between the payor and beneficiary’s account1cbdcs: An opportunity for the monetary system. The Bank for International Settlements. (2021, June 23). Retrieved February 3, 2023, from https://www.bis.org/publ/arpdf/ar2021e3.htm.
How Does a Retail CBDC Transaction Work?
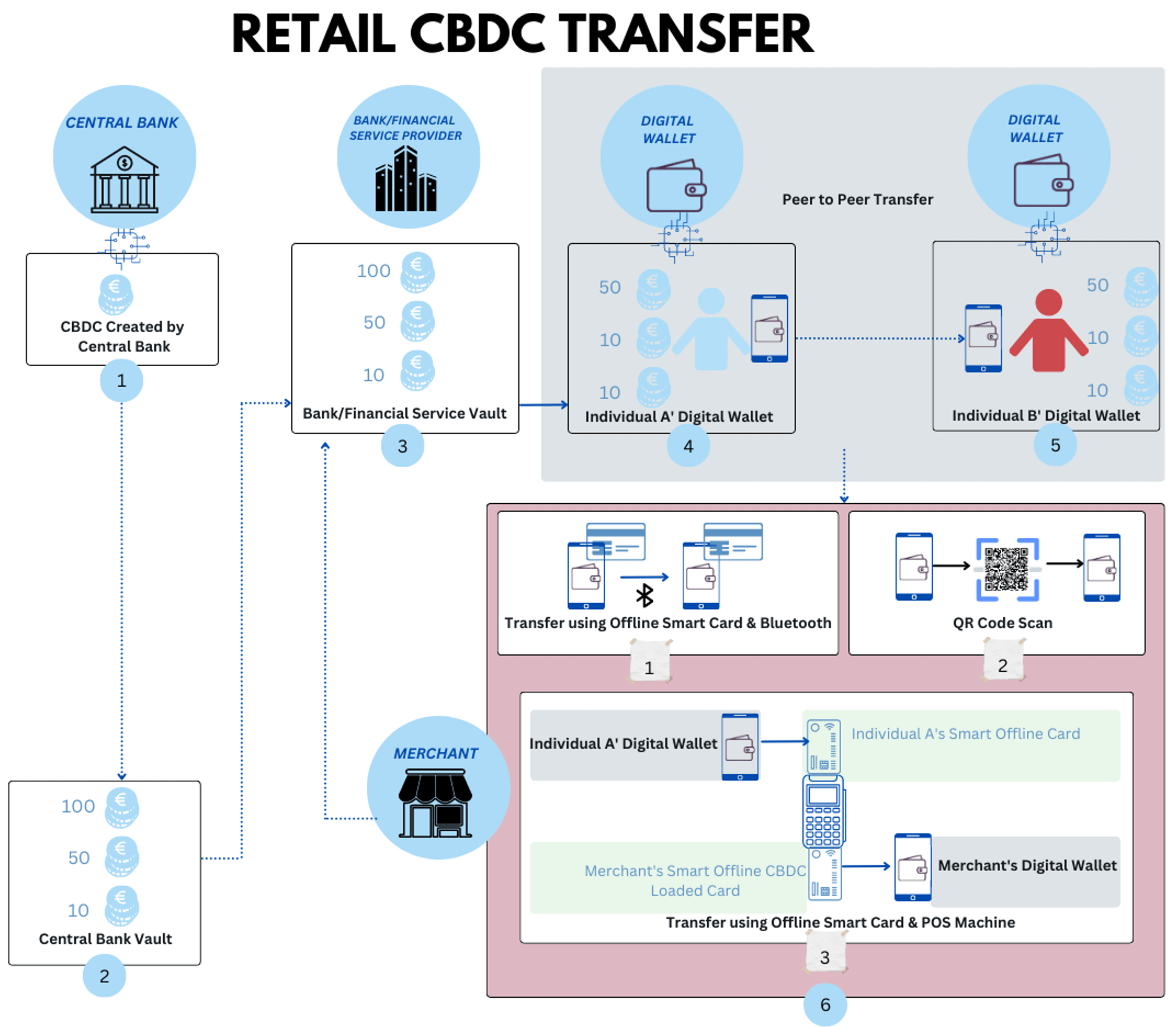
Following are the various actions performed while executing a CBDC Transaction
Issuing of CBDC by Central Bank to Financial Service Provider
Depending upon the model, Central Bank wants to follow, CBDCs shall be issued by the Central Bank’s vault to Financial Service Provider’s vault.
Creation of CBDC by Central Bank
CBDC’s are initially created/minted by the Central banks on a blockchain ledger. The underlying technology shall be either a Centralized Distributed ledger or Permissioned Distributed Ledger.
Withdrawal of CBDC in an Individual’s Digital Wallet
A user, on-demand, can request a withdrawal from the balance kept with Financial Service Provider to his/her digital wallet for spending at a merchant store or peer-to-peer transfer
Initiation of the Transaction
Peer-to-Peer Transfer
An individual can easily transfer the CBDC from one digital wallet to another individual’s Mobile Digital Wallet Application. This type of transfer is called as Peer to Peer Transfer2Reserve Bank of Australia. (n.d.). Retrieved February 3, 2023, from https://brs.website.rba.gov.au/publications/bulletin/2020/sep/pdf/bulletin-2020-09.pdf.
Transfer to Merchant
An individual can transfer retail CBDC to a merchant using:-
1) Transfer by Scanning the Merchant’s QR Code
2) Transfer using Smart Cards and Bluetooth
In this method, individual A transfers retail CBDC from a digital wallet application to Offline Smart Cards . This smart card is kept next to the mobile where offline CBDC transfer application like G+D Filia is open both for merchant and Individual. Thereafter, the Bluetooth is turned on by the individual A, and the merchant’s Bluetooth is selected, and the transfer is initiated.
3) Transfer using Smart Card and POS Machine
This is almost same as ‘Transfer using Smart Cards and Bluetooth’ however in this method, instead of using Bluetooth, Point of Sale (POS) Machines are used.
Validation of Transaction
Once an individual who already has CBDC in his/her wallet or account, wants to transfer it to the vendor or another individual, the transaction will be first validated on the distributed ledger technology or a private ledger network (underlying technology of the ledger used for transaction). Following are the various checks done while validating the transaction: –
1) Validation of the identity of the individual initiating the transaction and the recipient
2) Availability of funds
3) Authenticity of the funds
4) KYC stands for Know Your Customer and AML/CFT stands for Anti Money Laundering/Combating Financing of Terrorism. The CBDC transactions processed are done taking into consideration the KYC-AML/CFT laws set by the country and IMF to counter the illicit flow of funds.
Ledger Update
A ledger is a database of monetary holdings, which gets updated when a CBDC transaction is initiated. The debit and credit transactions both get updated on the ledger as soon as the transaction is complete.
Final Payment
As soon as the ledgers are updated, the beneficiary account starts showing the amount transferred by the payor. The backend payment advice for a transfer shall look like below.
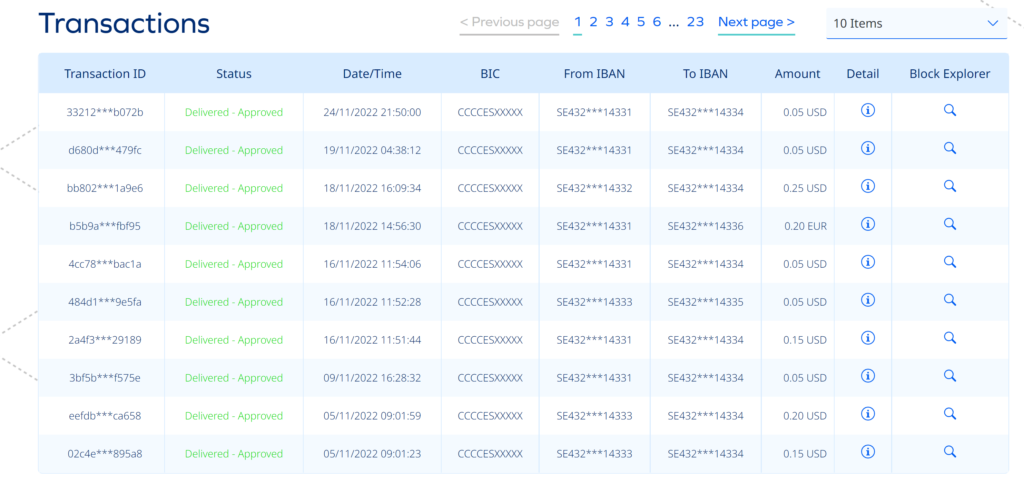
CBDC Retail Transaction Backend – Source
A working example of retail CBDC is e-Rupee CBDC, which is a retail CBDC launched by the Indian Government.
Why Retail CBDC?
Tokenization
Retail CBDC shall help in the tokenization of the money in circulation. This shall help in bringing efficiency to the payment infrastructure.
Tracking the Movement of Money
As of now, there is no easy way for the Central Banks to know what the exact money in circulation is and it’s very difficult to track the movement of the money. With each retail CBDC transaction getting recorded on a blockchain ledger, it will be easy for the central bank to check.
Cost of Transaction
Currently, the cost of a transaction using a credit card is quite high and merchant needs to pay a considerable percentage of commission for each transaction. Retail CBDC transactions intend to be competitive against the private players in the market and reduce the burden on the merchants for the transaction
Cashless Society
To avoid liquidity issues, as witnessed during the 2008 crisis and during the Covid era when the ATMs and commercial banks dried up, retail CBDC shall serve a perfect role in maintaining cash circulation in the market.
Micro Payments
A reader surfing through a magazine or a news website wants to read only a single article instead of buying a monthly subscription however currently it is very difficult to charge a small amount for example 2 cents or 10 pennies for reading a piece of article because of the commissions set by the intermediary payment gateways. With retail CBDCs, it will be easier to charge a tiny amount to the reader.
Government Aid Directly in the Account of the Beneficiary
If a grant/subsidy needs to be given to an individual from the government, currently it needs to be passed through the government office which makes the processing, time-consuming and involves corruption sometimes. With Retail CBDC, the grants/subsidy shall be transferred directly into the beneficiary’s digital wallet.
Tax Collection at POS (Point of Sale)
Retail CBDCs can be programmed to deduct tax, from the payment when made using retail CBDC, from a buyer to the merchant. This can help in avoiding lengthy tax reconciliations and filing procedures.
Tackling Counterfeit Currency
Various illicit groups across the world counterfeit currency notes by printing them illegally and using them for crime and terrorism. Since Retail CBDC shall be a digital version of currency bill notes, with underlying blockchain technology and robust infrastructure, therefore it shall not be possible for these illicit groups to continue such illegal activities.
Offline Retail CBDC Payment Capability in Case of a Power Outage
CBDC has the capability to transact offline. Check out here for more details
Can I Load Retail CBDC in my Wallet, Travel Abroad, and Spend?
Retail CBDC loaded in your wallet, for example, the digital dollar can only be spent in the US however if a US citizen had to travel abroad to the United Kingdom, he/she might need to connect the digital wallet to a foreign exchange, convert the US Digital Dollar CDBC into UK Pound CBDC and load it in the wallet. Thereby the individual shall be able to fly to the UK and start spending by scanning the merchant’s QR code3Cross-border payments for central bank digital currencies via universal … (n.d.). Retrieved February 4, 2023, from https://usa.review.visa.com/content/dam/VCOM/global/ms/documents/veei-cross-border-payments-for-cbdcs.pdf
How will it be On the Day of the Launch of Retail CBDC?
A clear plan has not been laid out by any central banks however it seems that on the day of the launch of Retail CBDC, applications for applying for digital wallets will open which shall require an individual to clear the KYC and thereby convert the money kept in a commercial bank, into the retail CBDC either directly through Central Bank or authorized intermediatory. This shall bring the converted retail CBDC into the digital wallet. There shall be a limit also put up initially to convert the money kept in a commercial bank to retail CBDC to efficiently distribute the CBDC to the public4Kashyap, H. (2022, November 19). RBI set to launch retail CBDC soon. Inc42 Media. Retrieved February 4, 2023, from https://inc42.com/buzz/rbi-set-launch-retail-cbdc-soon/
Summary
Depending upon the model decided by the country’s Central Bank, either the Central Bank itself or a private player can manage the user interface and support for the wallets, CBDC accounts, and CBDC transactions. Further, regulations shall be set by the Central Bank and the government on the level of anonymity required while dealing with transactions and user data.
References